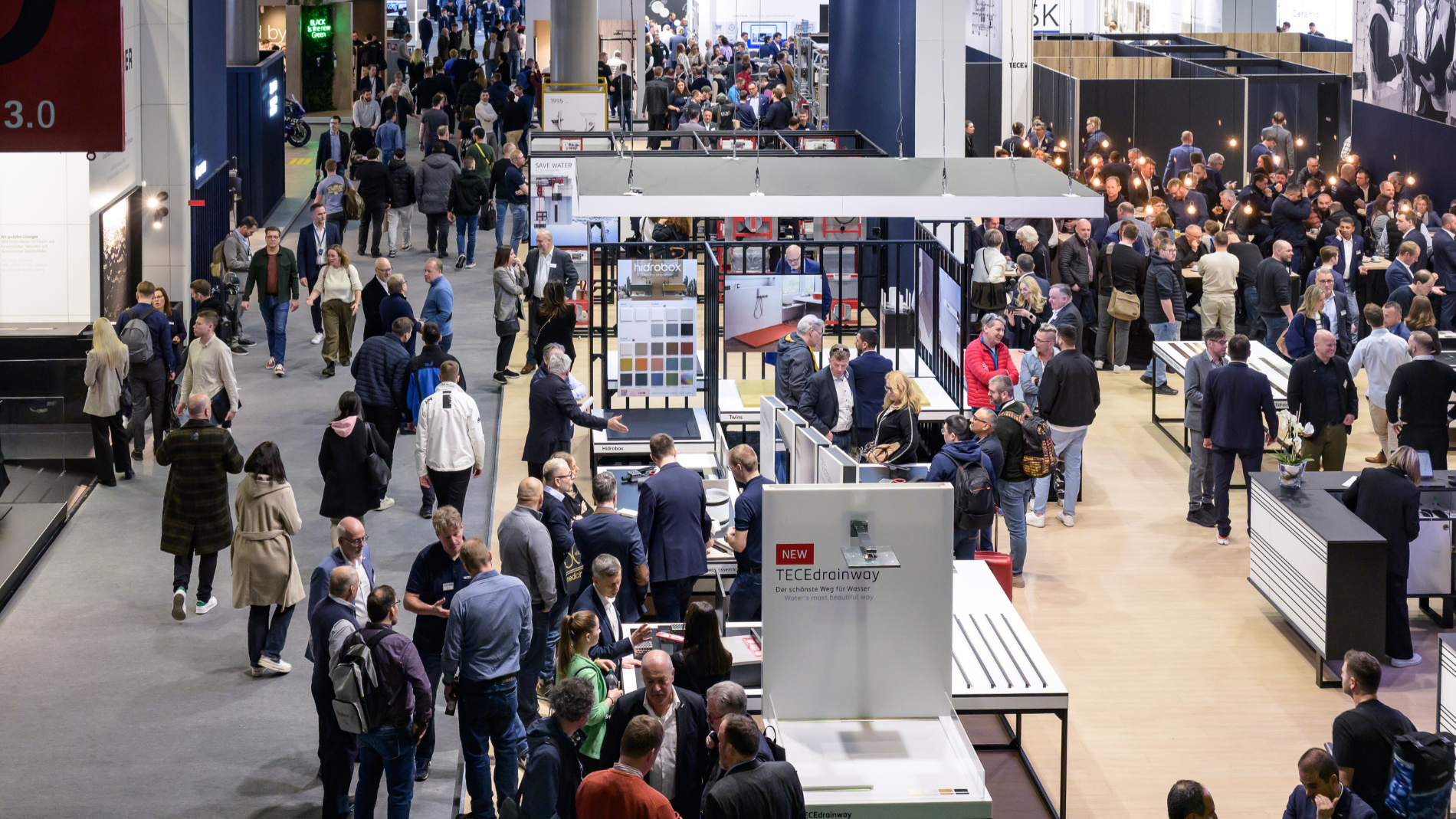
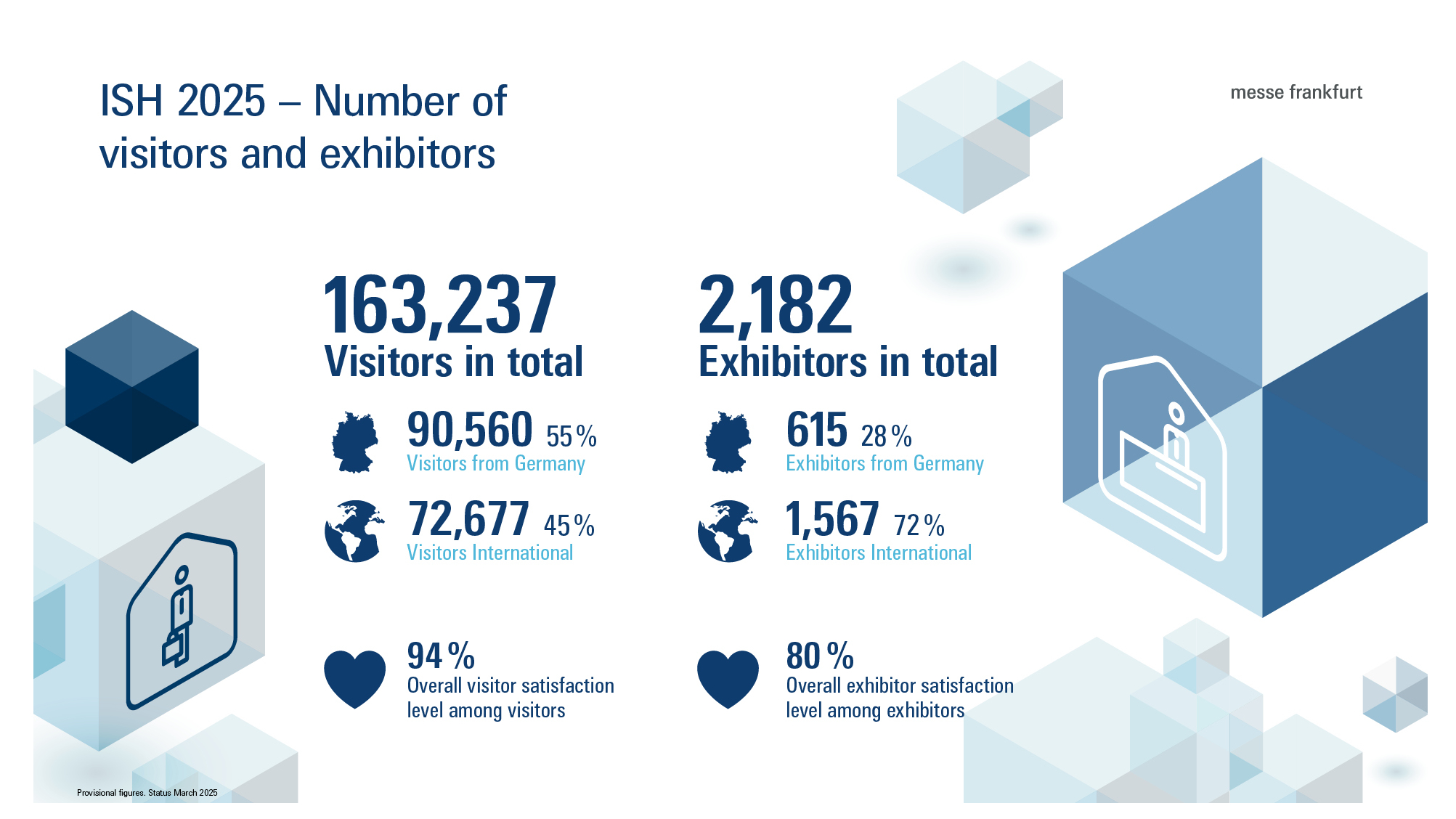
As the world’s leading trade fair for HVAC + water, ISH is where the HVAC and sanitation industry shares what truly drives progress. In 2025, more than 163.000 experts from 149 nations gathered in search of partners, products and solutions for a sustainable future.
Solutions for a sustainable future
ISH meets the growing demand for comfort, convenience, individualisation, well-being and aesthetics. Integrated solutions are able to cover all these requirements and make a decisive contribution to energy efficient and resource-friendly building systems.
ISH, the leading international trade fair for the industry, focuses on solutions for a sustainable future:
Frankfurt welcomes the entire sector – you’ll find all key target groups at ISH:
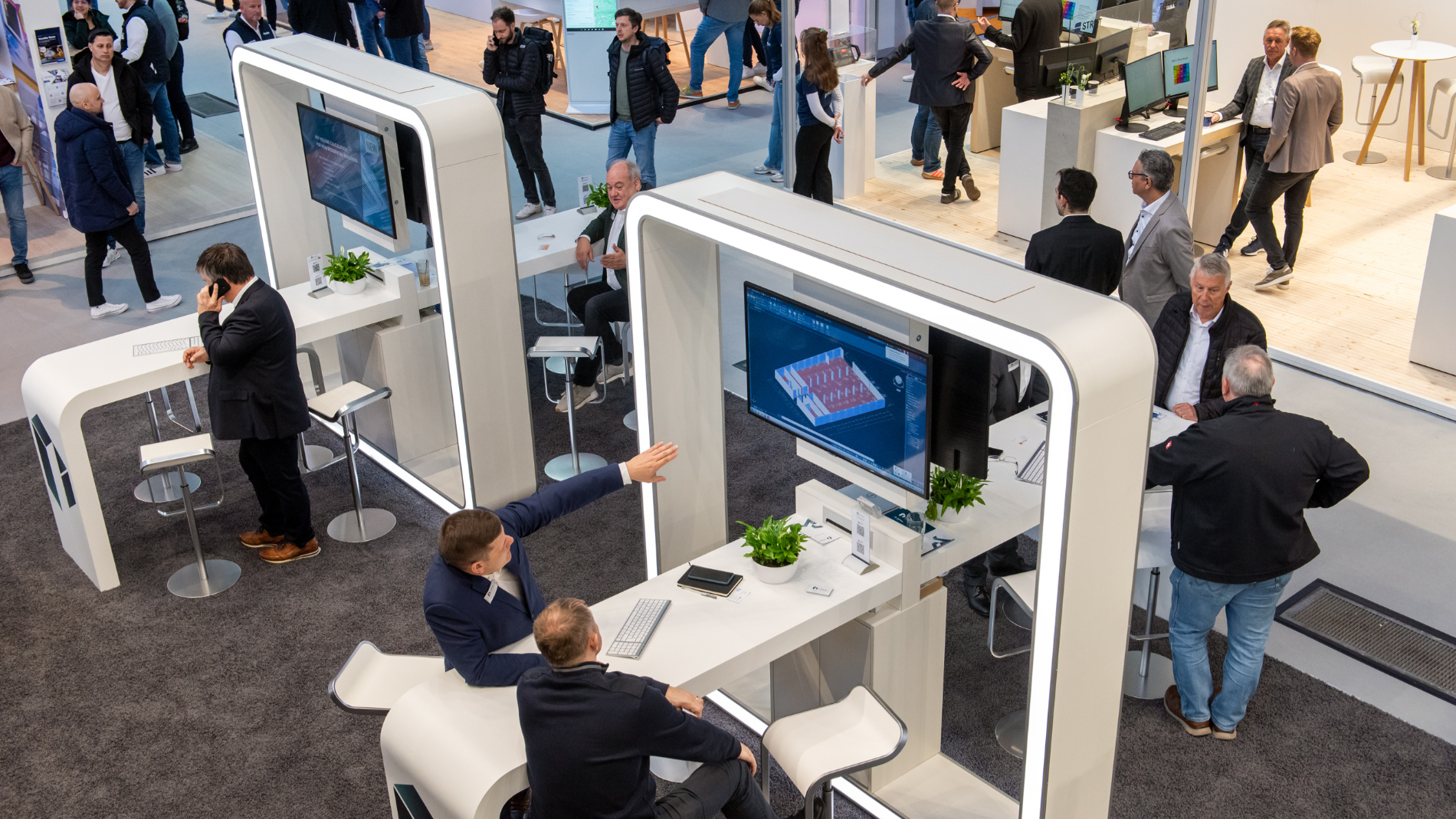

- Sanitation, heating and air-conditioning installers and industry
- System planners and engineers
- Wholesalers and retailers
- Architects, interior architects, designers
- Construction and housing industry
- Investors and local authorities